Scalper1 News
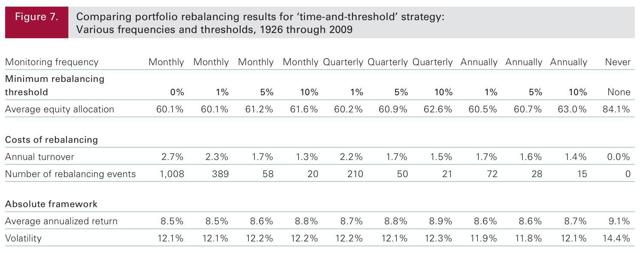
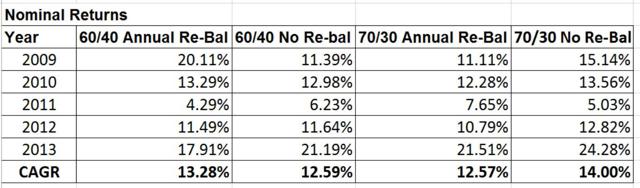 It’s that time of year again. Time to look at your portfolio and decide on your rebalancing strategy. Most investors know they should rebalance but many don’t do it or they get hung up on the detailed mechanics of rebalancing. In this post I’ll present a quick summary of rebalancing approaches and share my approach as well. We rebalance portfolios to improve risk adjusted returns over the long haul. In general, if portfolios are not rebalanced then the equity portion of the portfolio grows to dominate the overall portfolio and its risk. This is usually not something investors want especially as they age. After the decision to rebalance, the next question is how often. The frequency of rebalancing has to be traded off with the costs of rebalancing, transaction fees, commissions, etc… We also need to consider if we should rebalance if there is any difference at all in our target percentage allocations or wait until there is a significant enough difference to trigger an allocation decision. Say your target is 60% stocks and at the end the year you end up at 61% stocks. Does the benefit of rebalancing outweigh the costs? Probably not in this case. So, how does an investor choose the best approach? Fortunately, the great folks at Vanguard have done all the heavy lifting for us in this paper. Here is the summary table. (click to enlarge) As the above table shows basically there is not a big difference in rebalancing approaches, outside of never rebalancing. Even a monthly rebalance with a 0% threshold does not increase portfolio turnover and costs as much as you would expect. The last column also shows the results of never rebalancing – higher returns but with significantly higher volatility which leads to portfolio outcomes that most investors cannot stick with over time. These results also hold for quant portfolios. Whether implementing the IVY portfolios, the Permanent portfolios, Quant portfolios, the timing and threshold of the rebalance does not make a significant difference to long-term portfolio returns, e.g. see the IVY portfolio FAQ question #4. However, it is important to point out that there are periods where rebalancing does not work. Let me give you an example. The table below compares the returns of 60/40 stock bond and 70/30 stock bond portfolios with yearly rebalancing and no rebalancing over the last 5 years (2009 to 2013). (click to enlarge) As the table shows, yearly rebalancing increased returns for the 60/40 portfolio but yearly rebalancing actually decreased returns for the more aggressive 70/30 portfolio. This is typical in strong bull markets when stocks consistently outperform. This is maybe one of the reasons investors abandon rebalancing. But it is important to focus on the long term and more importantly on risk adjusted returns and stick to a rebalancing strategy. Personally, I rebalance once a year with a 1% threshold across all my portfolios regardless of strategy. But that is what I have found works for me. The best advice I can give anyone is to paraphrase the Vanguard advice – choose a regular periodic rebalancing approach that fits your investment style and that you can stick with over the long haul. This is most likely my last post for this year. Hope everyone has a Happy New Year! Here is to a great and prosperous 2015. At the beginning of the year I’ll be focusing on updating all the yearly returns for all the portfolios and strategies I track. I’m looking forward to sharing the results with everyone. Scalper1 News
It’s that time of year again. Time to look at your portfolio and decide on your rebalancing strategy. Most investors know they should rebalance but many don’t do it or they get hung up on the detailed mechanics of rebalancing. In this post I’ll present a quick summary of rebalancing approaches and share my approach as well. We rebalance portfolios to improve risk adjusted returns over the long haul. In general, if portfolios are not rebalanced then the equity portion of the portfolio grows to dominate the overall portfolio and its risk. This is usually not something investors want especially as they age. After the decision to rebalance, the next question is how often. The frequency of rebalancing has to be traded off with the costs of rebalancing, transaction fees, commissions, etc… We also need to consider if we should rebalance if there is any difference at all in our target percentage allocations or wait until there is a significant enough difference to trigger an allocation decision. Say your target is 60% stocks and at the end the year you end up at 61% stocks. Does the benefit of rebalancing outweigh the costs? Probably not in this case. So, how does an investor choose the best approach? Fortunately, the great folks at Vanguard have done all the heavy lifting for us in this paper. Here is the summary table. (click to enlarge) As the above table shows basically there is not a big difference in rebalancing approaches, outside of never rebalancing. Even a monthly rebalance with a 0% threshold does not increase portfolio turnover and costs as much as you would expect. The last column also shows the results of never rebalancing – higher returns but with significantly higher volatility which leads to portfolio outcomes that most investors cannot stick with over time. These results also hold for quant portfolios. Whether implementing the IVY portfolios, the Permanent portfolios, Quant portfolios, the timing and threshold of the rebalance does not make a significant difference to long-term portfolio returns, e.g. see the IVY portfolio FAQ question #4. However, it is important to point out that there are periods where rebalancing does not work. Let me give you an example. The table below compares the returns of 60/40 stock bond and 70/30 stock bond portfolios with yearly rebalancing and no rebalancing over the last 5 years (2009 to 2013). (click to enlarge) As the table shows, yearly rebalancing increased returns for the 60/40 portfolio but yearly rebalancing actually decreased returns for the more aggressive 70/30 portfolio. This is typical in strong bull markets when stocks consistently outperform. This is maybe one of the reasons investors abandon rebalancing. But it is important to focus on the long term and more importantly on risk adjusted returns and stick to a rebalancing strategy. Personally, I rebalance once a year with a 1% threshold across all my portfolios regardless of strategy. But that is what I have found works for me. The best advice I can give anyone is to paraphrase the Vanguard advice – choose a regular periodic rebalancing approach that fits your investment style and that you can stick with over the long haul. This is most likely my last post for this year. Hope everyone has a Happy New Year! Here is to a great and prosperous 2015. At the beginning of the year I’ll be focusing on updating all the yearly returns for all the portfolios and strategies I track. I’m looking forward to sharing the results with everyone. Scalper1 News
Scalper1 News