Investing In Africa: A Long-Term Growth Opportunity?
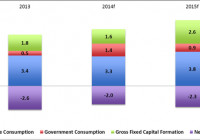
Summary Certain indicators point to an overvalued S&P 500. Prudent investors should consider more attractively valued indexes. Despite headwinds, Africa’s improving fundamentals suggest long term growth opportunities. As the new year begins to take shape, most investors have their attention squarely focused on the United States as the oasis of growth in a desert of underperforming national economies. Nevertheless, when we take a closer look at the key American stock market index, the S&P 500 (NYSEARCA: SPY ), it would appear that many market observers consider it to be overvalued. Some suggest that its blended P/E ratio of 17 is on the upper end of its historical normal valuation range since 2001, others warn that it is historically expensive relative to GDP and finally most point to the Shiller P/E which currently sits at 26.4, which is 59% higher than the historical mean of 16.6. Although it is difficult to make accurate broad valuation forecasts for a large collection of companies such as the S&P 500, such forecasts can be useful to the prudent investor. If we are willing to accept that many companies trading on the S&P 500 are trading at or above their fair value we may at minimum need to consider the possibility of a slowdown in broad index growth over the coming year. As such, the prudent investor may want to start contemplating other more attractively valued indexes. It would appear that such opportunities lie in Africa. Despite several headwinds such as the effects of the Ebola virus, civil unrest (Boko Harem), the slowdown in the global economy and the drop in the price of oil, Africa remains a resilient continent poised to record around +5% economic growth. In a recent report Yogesh Gokool, head of the AfrAsia Bank explains that this growth will be primarily driven by more foreign direct investments and remittances from non-OECD (Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development) countries that will continue to pour money into corporate acquisitions and large-scale infrastructure projects. Resource rich countries will continue to attract the lion share of FDIs into Africa yet with the drop in the price of oil and rising wages in Asia, manufacturing will also be a significant recipient. The other main driver of growth will be private consumption. In a recent report by the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa entitled African Economic Outlook 2015 it was found that private consumption in Africa is expected to accelerate by 0.5 percentage points to 3.8 percent in 2015 due to consumer confidence and the expanding middle class. Private Consumption and gross capital formation are expected to be key drivers of growth (click to enlarge) Data Source: UN-DESA, 2014 In addition, inflation should remain under control by 0.4 percentage points to 0.7 in 2015. Subdued inflation across economic groupings (click to enlarge) Data Source: UN-DESA, 2014 As for fiscal deficits, the current account balance is expected to decline but remain positive for oil exporting countries while the current account deficit may rise less than expected due to lower oil prices for oil importing countries. Moderating fiscal deficits expected in 2015 among country groupings (click to enlarge) Data Source: EIU, 2014 As mentioned above, certain downside risks could slow economic growth in Africa such as the effects of the Ebola virus, civil unrest (Boko Harem), the drop in oil and commodity prices and a global growth slowdown. Based on early assessments , the economies of Guinea, Liberia, Sierra Leone are experiencing significant hardship as public finances are strained and household incomes are dropping. Nevertheless, the economic impact is not as bad as some feared as the World Bank estimated that Ebola could cost the region as much as $32 billion and the real cost appears to only be a tenth of that figure. In fact, a positive impact of the outbreak seems to be the renewed urgency to reinforce basic public health systems in vulnerable regions. As for lower commodity prices, the negative impact on the continent’s growth may be offset as lower prices will help ease balance of payments pressures in food and energy importing countries while commodity exporting countries face lower export earnings. Furthermore, these commodity declines will serve to reaffirm the benefits of more diversified national economies. Finally, in the face of a potential global slowdown Africa should remain attractive as its economic fundamentals remain sound . Governance and macroeconomic management have improved. Investment in infrastructure, human and physical capital are increasing. Productivity, the middle class and diversified trade are all growing and finally a culture of entrepreneurship is being created. Conclusions Given the risks outlined above and my belief that stable growth in Africa is still a long way off, it may be better to describe investing in Africa as an opportunity for the enterprising investor rather than the prudent investor. Nevertheless, if you remain patient and take a long-term view of an investment in Africa, you may be interested in several ETFs which have African exposure and are currently trading near their 52 week lows. The first is the Market Vectors Africa Index ETF (NYSEARCA: AFK ), which allocates just over a quarter of its weight to developed market countries that do business in Africa. This allocation serves to reduce some of the fund’s exposure to the volatility of local African markets. The fund is heavily weighted to South Africa, Egypt and Nigeria with financials accounting for around 40% of the fund while materials and energy account for around 30%. The other ETF of note is the Guggenheim Frontier Markets ETF (NYSEARCA: FRN ). This fund invests in a collection of small, illiquid and risky markets with great growth potential known as frontier markets . These often high yielding markets have become an asset class in their own right and the fund’s exposure to Africa is only about 13%, with the rest allocated to other markets in Latin America.