Long Duke, But Don’t Load Up Just Yet
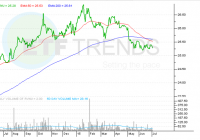
Summary An abnormal growth trend in the past two years has caused a relatively stable industry to see much decline due to energy conservation and a lack of overall demand. Bad PR surrounding the new EPA rulings on carbon pollution and coal ash have created nightmares for Duke, resulting in a 10% decline on the year. Capitalization on the higher demand for energy during the summer could help bolster the stock short-term, along with a potential share buyback. Achieving the EPS, setting a greater growth trend for the dividend, keeping the credit ratings high, and EPS growth at least a 5% for the long-term are all pivotal to. After viewing the dividend hike to 82.5 cents a share and sifting through some high short interest stocks, I came across a well-known name: Duke Energy (NYSE: DUK ). Deep in the integrated utilities, the Charlotte -based energy company is a long-time energy producer suffering from a poor growth trend due to a lagging commodities sector and lethargic demand. The company deserves a hold rating, as very few growth catalysts are leadings its outlook. Having only had a positive FCF since 2012, now in the amount of $1.09 billion on a LTM basis, I’m concerned that the recent dividend raise might eat too significantly into FCF. Furthermore, with Lynn Good increasing her salary by 50%, but more notably her short and long-term incentive opportunities to higher multiples of her salary, I believe the money could be better well-spent given their lagging growth recently. Sure, they did implement a new retirement program , but again, there are bigger problems that Duke is facing besides employee turnover. As I figured, the stock saw a lot of downward momentum at the end of the winter, and has really just been on a slow down trend since the spring started. We’re seeing really interesting support around the $70 level. The stock is at April 2013 levels, where they were fairing much the same as they are now. The second half of 2014 proved to be an exceptional growth trend, just about scraping the $90 level, but I can’t reasonably expect the stock to trend in that direction for quite some time. (click to enlarge) Source: Bloomberg We’ve seen a good, but not great three year revenue growth trend from Duke, with most of the gains coming in 2012. With revenues now well above $25 billion, I’m concerned that they won’t be able to sustain this level. Their International Energy segment has seen a small decline of 1.15% over the past three years, which accounts for about $1.4 billion in revenue each year. While much of their efforts are concentrated in Latin America, Brazil has been of particular interest to the company. Much of the operations are similar to their domestic segment, Brazil is suffering from a poor wet season and high water demand, causing reservoirs to be low and inefficient for their hydropower plants. Furthermore, I can’t see them having huge international growth when things like their quarter interest in National Methanol Company (NMC) in Saudi continues to suffer from extremely low margins. Luckily, International Energy does not account for a substantial portion of total revenue, but it’s worth noting that hydropower in Brazil will be lower in future quarters based upon thermal power being prioritized over hydropower and this trend will continue through the end of the year, already down 52.9% in terms of pricing. Sure, there are a few construction and renovation projects that Duke has going for them, but they’re not going to see the light of day until three or four years out, let alone reach their highest potential capacity. For example, a 750 MW natural gas-fired generating plant in South Carolina, which cost about $600 million, won’t be available for use until late 2017 ( 10-Q ). Even little things like the switching from lead acid to lithium-ion batteries in the Notrees Windpower Project in Texas are important steps in helping long-term efficiency and stability for the company. They just recently gained a 40% stake in the $5 billion venture to build the Atlantic Coast Pipeline, which will bring natural gas from Marcellus and Utica in Pennsylvania to West Virginia and coast Virginia and then to North Carolina. Additionally, a 1640 MW combined cycle natural gas plant in Citrus Country Florida, expected to be finished in 2018, will cost $1.5 billion. Based upon hedging activities from many oil companies, like Oasis Petroleum (NYSE: OAS ), running out next year, the input fuel could be very cheap to Duke. On a different note, the stock repurchase program that began earlier this year still has about 15% left approved, which represents a good buyback of about $225 million. This will certainly help push the shares up for a few sessions. The Commodities Caveat Apart from construction and financial growth catalysts, which will have seemingly minimal effects, the commodities market could really end up hurting this company if prices rise. While natural gas prices, via the Henry Hub below, have been on a great YOY downtrend, which reduces input costs, there’s a caveat present. (click to enlarge) Source: Bloomberg With an oversupply of natural gas and plants at Duke reaching 94% capacity, they’re going to suffer from limited profitability. Revenues will eventually decline due to a lower margin received for their output. While demand for natural gas isn’t increasing, but is rather just being adopted as coal-based energy retreats, Duke could have a real profitability problem on its hands, considering their profit margin is expected to drop over 9% this year. The exact same case applies to oil and company management has estimated that the negative effects will be anywhere from 2.5-5% of EPS. I firmly believe their operating margin will remain strong around 24%, but I would need to see significant improvement for this utility company to fend off tough macro conditions. Speaking of said conditions, with a proposed interest rate hike from the Fed later this year, company management has stated that EPS could be affected as much as -$0.07 in the following quarter. Need For Improvement I firmly believe that their regulated utilities segment needs to start showing growth before a reasonable entry point can be made into the stock. Accounting for $22.2 billion in total revenue, the entire segment is up about 27.92% in the past three years, but this has already been priced into the stock, considering many of the gains took place in FY 2014 and FY 2012. Their primary servicing region of the Carolinas, Florida, Ohio, Kentucky, and Indiana has about 7.3 million retail customers. Yet, take a look at the factors hampering their growth: Energy efficiency and conservation efforts, particularly in residential areas The Midwest and Carolina servicing regions were lagging; residential growth, overall, was down 1.4% A higher amount of unserviceable calls than normal this past winter and an increasing number of outages this summer Their commercial power segment, which really only represents a fraction of a percent of total revenue, has suffered a 53.22% three-year decline. Their focus, here, is on alternative energy sources, primarily wind and solar. Regulation Woes Rising Regulation via the EPA’s “Clean Power Plan” set to cut carbon pollution for power plants by 30% by 2030 will pass this summer ( Bloomberg ). This effectively eliminates a coal from being the major energy generator in the long-term, as now the cost structure is unfavorable. Coal Ash Disposal has become a recent nightmare for Duke as they are now required to dispose of the coal ash at four major sites sustainably by 2019 and have all sites cleared by 2029. CBS’ 60 Minutes even dedicated an entire segment towards criticizing the current disposal process of Duke. The estimated cost is about $3.4 billion, or about 3x FCF, currently. Again, the company will still be fine in the long-term as they have a current available liquidity of $6.4 billion, and while they could use a bump up in their credit ratings, the company is standing on solid ground. (click to enlarge) Source: Company Presentation Conclusion On the back end, Duke may benefit from higher D&A costs when it comes time for quarterly reports based upon the pipeline and construction activity, Duke Energy will report quarterly earnings on August 6th, just after the end of July surge of earnings reports from major oil and gas companies. It’s worth noting that their Q3 EPS levels have been historically higher than all other calls, and with projections showing a potential 50% increase in EPS from Q2 to Q3 of this year, the stock is definitely worth considering. Looking to the future, I believe this company will most likely be fine – but there’s too much short-term negativity clouding any decent chance at profitability. Note: All Financial Data Taken From Bloomberg Database Disclosure: I/we have no positions in any stocks mentioned, and no plans to initiate any positions within the next 72 hours. (More…) I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.