Scalper1 News
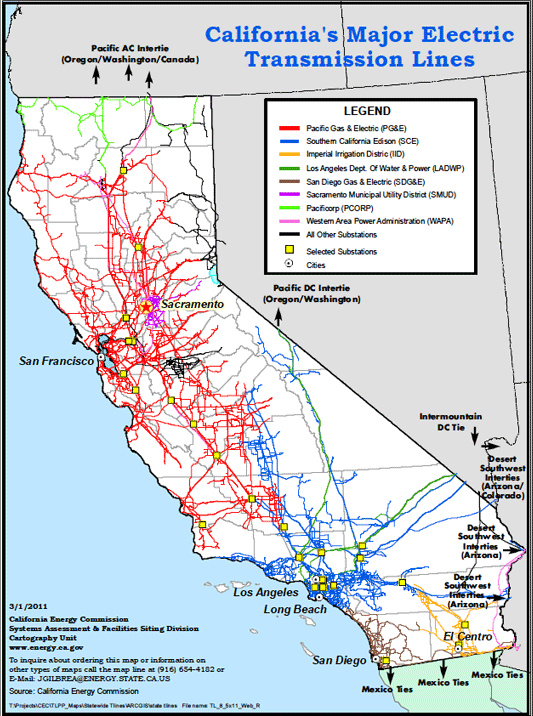

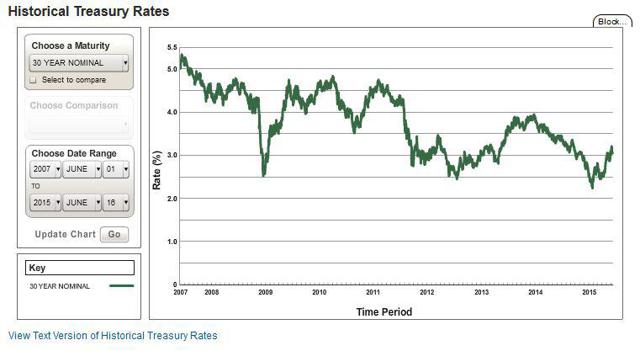
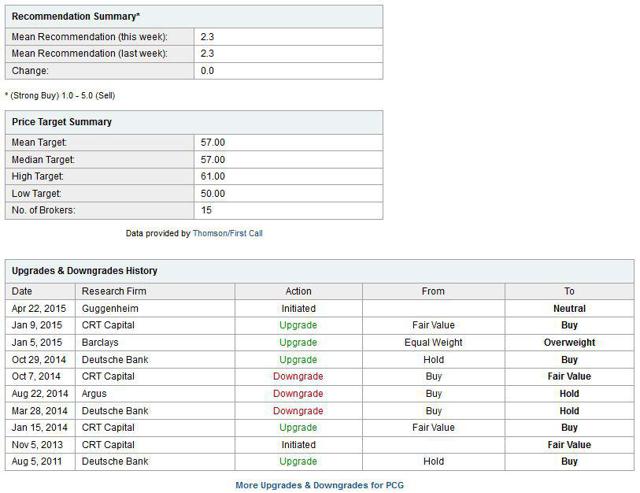
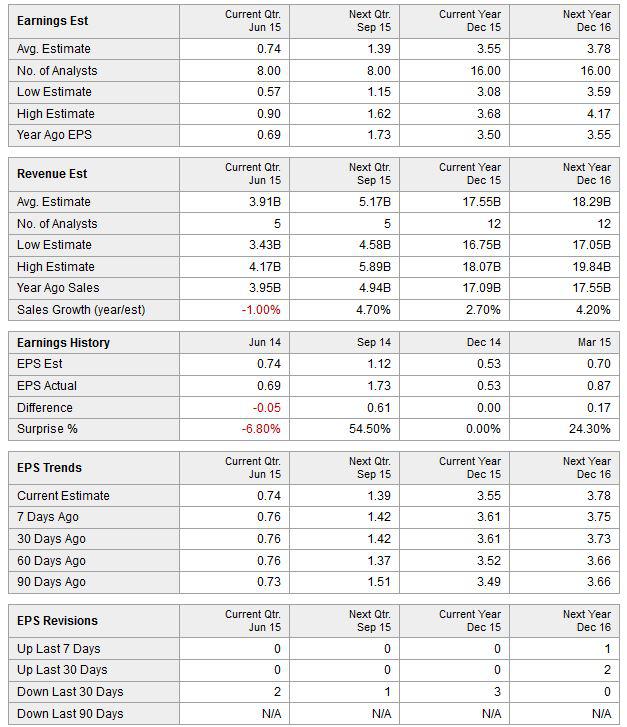 Summary PG&E is coming off a rough patch with some legal troubles. The interest rate environment is favorable, and PG&E is heavily leveraged. PG&E’s cost of production has declined due to the low cost of energy. Experts have mixed opinions on the stock, but are more bullish long-term. The low interest rate environment coupled with low energy prices is a best case environment for Pacific Gas & Electric (NYSE: PCG ). The utility can use low interest rates to roll over their existing debt and use low energy prices to hedge costs of production at a historically low rates. Not all is rosy, the utility must navigate a complex and tangled legal environment, and placate concerns regarding energy grid security. Even through all these complications, PCG must continue to look forward and embrace innovation if it hopes to achieve its 2020 mandate that 33% of all power is from renewable sources. If PG&E can navigate the risks and take advantage of this favorable business environment, the company should continue to lead the U.S. utility sector. Market Overview PG&E Corporation is a public utility holding company, which means it is subject to regulatory oversight and must provide the regulatory body access to their records and books. The regulatory environment is tangled and complex, different sections of PCG’s business are regulated by one or more of these regulatory bodies: The CAISO , FERC , NRC , CPUC , and CEC . From FERC, which regulates the interstate transmissions of electricity and natural gas, to CEC, which handles energy policy and planning for the state of California. Regulation is central to a utility company like PG&E, even product pricing is done through a ratemaking process with regulators. Ratemaking is when a public utility company, like PCG or FERC, exchange information about the cost of energy production, operating expenses, and regulatory policy goals. Then the two agree on a price rate for energy which will cover all of these costs and provide a ‘fair’ rate of return. The market for energy is not competitive and is centralized is because of the large capital investment required for energy infrastructure and for real-time regulatory oversight. The government would have a difficult time regulating thousands of small electricity companies and it is possible policy demands for infrastructure would not be met. See here for more about how the California energy system works. Business Overview PG&E was founded in 1905 and continues to lead the United States as the largest utility company. The utility currently employees 22,581 people and operates mostly in northern California. The utility is diversified across many energy sectors, with nuclear generation facilities, combined cycle gas turbine electricity generators, wind power installations, natural gas pipeline and even energy storage. PG&E is a legal monopoly because of the strategic advantages of scale in the public utilities sector. Because PG&E is defined as a public utility company, many of its business choices are monitored closely or mandated by the federal and state governments. When making business changes, PG&E must move very deliberately in order to move in step with policy makers. Recently PG&E has been mandated to provide 33% of all energy from renewable sources by 2020. As you can see below, the Utility still has to acquire more renewable resources to achieve the mandate. Further the regulatory bodies have placed a growing target for energy storage. (click to enlarge) PG&E is heavily leveraged in the credit markets, because energy infrastructure is capital intensive and the payoff over long time horizons. Due to the Utility’s stability for more than a century, PG&E has been able to demand favorable terms for credit. Further, PG&E’s main products, consumer natural gas and electricity, are tied to the prices of oil and natural gas. These two energy markets are near historic lows and PG&E should be able to hedge their energy costs for the next few years at favorable prices today. (click to enlarge) Growth Plan (From the Company’s 10-K ) Managing Legal risks: The Utility has many legal risks which are outlined in the Risk section below, it is vital that the Utility effectively manage these legal disputes or future growth could be inhibited. Renewable Power Initiatives: California law requires the Utility to gradually increase the amount of renewable energy to at least 33% of their annual retail sales by 2020. Natural Gas Pipeline: During 2014 the Utility completed its system wide replacement of 847 miles of iron pipelines with plastic pipe. Energy Storage: California law has established initial energy storage targets for the Utility. The Utility currently has 80.5 MW of energy storage which meets the target. The target is expected to increase over the next few years. Additional Transmission: The Utility plans to complete a new transmission line connecting the Gates and Gregg substations. The new line is expected to reduce the number and duration of power outages, improve voltage in the area and increase economic activity in the area. Additional Distribution: In October 2014, the Utility began operations at the first of three new electric distribution control centers. These centers will utilize Smart Grid technologies for added stability to the grid. Risks (From the Company’s 10-K ) Enforcement matters, investigations, regulatory proceedings: The environment for legal risk for PCG is sizable, with a federal criminal prosecution of the Utility. Additionally the rates and tariffs which PCG can charge customers is set by the government through a legal process. Liquidity and Capital Requirements: Since PCG has been around more than a century their credit rating stable, however, the inability to continue to attract favorable lending rates would greatly reduce the profit of PCG. Operations and Information Technology: There are broad array security and cybersecurity risks which come with operating a large utility company. The majority of these risks deal with containment of large accidents, adverse weather preparation and sensitive data protection. Environmental Factors: Both the macro economic environment as well as the physical environment have large impacts on the performance of PCG. Extremely hot summers cause more demand which strains the electricity grid, while extremely cold winters strain the natural gas network. PCG must continue to upgrade the infrastructure of the Utility in order to mitigate these environmental risks. Competition From New Technology: The Utility is subject to increased competition due to the increasing viability of distributed generation and energy storage technologies. The levels of self-generation of electricity by customers (mainly solar) and the use of customer net energy metering, which allows self-generating customers to receive bill credits at the full retail rate, are increasing. Expert Opinion (click to enlarge) Analyst opinion has moved from negative three years ago, to positive in the last year. The mean price target for PCG is $57 per share, which currently gives PCG stock an upside of approximately 10%. Analysts have moved down their EPS estimates over the last 90 days, which is a bearish sign for the stock’s near-term value. However, PCG has a tendency to surprise investors with its EPS announcements. In conclusion, analysts are uncertain about the near-term prospects of PCG, but they are bullish regarding the long-term value of the company. Current Events PG&E recognized by CIO magazine as a CIO 100 Award Winner Gas pipeline explosion near Fresno, CA, which led to a payout of $1.6 billion . A recent blackout in Berkeley, CA. Conclusion PG&E is a utility that is going through a near-term rough patch, but is well positioned to take advantage of long-term trends in the energy industry. Since PG&E requires credit to invest in energy infrastructure, the current low interest rates environment is useful for refinancing current loans and starting new projects at attractive credit rates. Further PG&E benefits from a low cost energy environment which allows them to hedge their costs of production at attractive rates. While PG&E is well positioned, the future growth of PG&E is dependent upon the Utility’s ability to mitigate risks. There are significant risks to growth which PG&E must overcome and manage if they wish to continue to lead the Utility sector. PG&E is exposed to a few major legal cases which could negatively impact the company. Further, the company must integrate renewable energy resources into the grid while maintaining stability. Analysts are aware of these risks and are divided regarding the future price of PG&E. In conclusion, PG&E the largest utility in the U.S. and is well positioned to take advantage of two major market trends if it can manage the risks. The utility should continue to lead the sector and is a buy if an investor is looking for dividend capture and stable growth in the U.S. utility space. Disclosure: The author has no positions in any stocks mentioned, and no plans to initiate any positions within the next 72 hours. (More…) The author wrote this article themselves, and it expresses their own opinions. The author is not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). The author has no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article. Scalper1 News
Summary PG&E is coming off a rough patch with some legal troubles. The interest rate environment is favorable, and PG&E is heavily leveraged. PG&E’s cost of production has declined due to the low cost of energy. Experts have mixed opinions on the stock, but are more bullish long-term. The low interest rate environment coupled with low energy prices is a best case environment for Pacific Gas & Electric (NYSE: PCG ). The utility can use low interest rates to roll over their existing debt and use low energy prices to hedge costs of production at a historically low rates. Not all is rosy, the utility must navigate a complex and tangled legal environment, and placate concerns regarding energy grid security. Even through all these complications, PCG must continue to look forward and embrace innovation if it hopes to achieve its 2020 mandate that 33% of all power is from renewable sources. If PG&E can navigate the risks and take advantage of this favorable business environment, the company should continue to lead the U.S. utility sector. Market Overview PG&E Corporation is a public utility holding company, which means it is subject to regulatory oversight and must provide the regulatory body access to their records and books. The regulatory environment is tangled and complex, different sections of PCG’s business are regulated by one or more of these regulatory bodies: The CAISO , FERC , NRC , CPUC , and CEC . From FERC, which regulates the interstate transmissions of electricity and natural gas, to CEC, which handles energy policy and planning for the state of California. Regulation is central to a utility company like PG&E, even product pricing is done through a ratemaking process with regulators. Ratemaking is when a public utility company, like PCG or FERC, exchange information about the cost of energy production, operating expenses, and regulatory policy goals. Then the two agree on a price rate for energy which will cover all of these costs and provide a ‘fair’ rate of return. The market for energy is not competitive and is centralized is because of the large capital investment required for energy infrastructure and for real-time regulatory oversight. The government would have a difficult time regulating thousands of small electricity companies and it is possible policy demands for infrastructure would not be met. See here for more about how the California energy system works. Business Overview PG&E was founded in 1905 and continues to lead the United States as the largest utility company. The utility currently employees 22,581 people and operates mostly in northern California. The utility is diversified across many energy sectors, with nuclear generation facilities, combined cycle gas turbine electricity generators, wind power installations, natural gas pipeline and even energy storage. PG&E is a legal monopoly because of the strategic advantages of scale in the public utilities sector. Because PG&E is defined as a public utility company, many of its business choices are monitored closely or mandated by the federal and state governments. When making business changes, PG&E must move very deliberately in order to move in step with policy makers. Recently PG&E has been mandated to provide 33% of all energy from renewable sources by 2020. As you can see below, the Utility still has to acquire more renewable resources to achieve the mandate. Further the regulatory bodies have placed a growing target for energy storage. (click to enlarge) PG&E is heavily leveraged in the credit markets, because energy infrastructure is capital intensive and the payoff over long time horizons. Due to the Utility’s stability for more than a century, PG&E has been able to demand favorable terms for credit. Further, PG&E’s main products, consumer natural gas and electricity, are tied to the prices of oil and natural gas. These two energy markets are near historic lows and PG&E should be able to hedge their energy costs for the next few years at favorable prices today. (click to enlarge) Growth Plan (From the Company’s 10-K ) Managing Legal risks: The Utility has many legal risks which are outlined in the Risk section below, it is vital that the Utility effectively manage these legal disputes or future growth could be inhibited. Renewable Power Initiatives: California law requires the Utility to gradually increase the amount of renewable energy to at least 33% of their annual retail sales by 2020. Natural Gas Pipeline: During 2014 the Utility completed its system wide replacement of 847 miles of iron pipelines with plastic pipe. Energy Storage: California law has established initial energy storage targets for the Utility. The Utility currently has 80.5 MW of energy storage which meets the target. The target is expected to increase over the next few years. Additional Transmission: The Utility plans to complete a new transmission line connecting the Gates and Gregg substations. The new line is expected to reduce the number and duration of power outages, improve voltage in the area and increase economic activity in the area. Additional Distribution: In October 2014, the Utility began operations at the first of three new electric distribution control centers. These centers will utilize Smart Grid technologies for added stability to the grid. Risks (From the Company’s 10-K ) Enforcement matters, investigations, regulatory proceedings: The environment for legal risk for PCG is sizable, with a federal criminal prosecution of the Utility. Additionally the rates and tariffs which PCG can charge customers is set by the government through a legal process. Liquidity and Capital Requirements: Since PCG has been around more than a century their credit rating stable, however, the inability to continue to attract favorable lending rates would greatly reduce the profit of PCG. Operations and Information Technology: There are broad array security and cybersecurity risks which come with operating a large utility company. The majority of these risks deal with containment of large accidents, adverse weather preparation and sensitive data protection. Environmental Factors: Both the macro economic environment as well as the physical environment have large impacts on the performance of PCG. Extremely hot summers cause more demand which strains the electricity grid, while extremely cold winters strain the natural gas network. PCG must continue to upgrade the infrastructure of the Utility in order to mitigate these environmental risks. Competition From New Technology: The Utility is subject to increased competition due to the increasing viability of distributed generation and energy storage technologies. The levels of self-generation of electricity by customers (mainly solar) and the use of customer net energy metering, which allows self-generating customers to receive bill credits at the full retail rate, are increasing. Expert Opinion (click to enlarge) Analyst opinion has moved from negative three years ago, to positive in the last year. The mean price target for PCG is $57 per share, which currently gives PCG stock an upside of approximately 10%. Analysts have moved down their EPS estimates over the last 90 days, which is a bearish sign for the stock’s near-term value. However, PCG has a tendency to surprise investors with its EPS announcements. In conclusion, analysts are uncertain about the near-term prospects of PCG, but they are bullish regarding the long-term value of the company. Current Events PG&E recognized by CIO magazine as a CIO 100 Award Winner Gas pipeline explosion near Fresno, CA, which led to a payout of $1.6 billion . A recent blackout in Berkeley, CA. Conclusion PG&E is a utility that is going through a near-term rough patch, but is well positioned to take advantage of long-term trends in the energy industry. Since PG&E requires credit to invest in energy infrastructure, the current low interest rates environment is useful for refinancing current loans and starting new projects at attractive credit rates. Further PG&E benefits from a low cost energy environment which allows them to hedge their costs of production at attractive rates. While PG&E is well positioned, the future growth of PG&E is dependent upon the Utility’s ability to mitigate risks. There are significant risks to growth which PG&E must overcome and manage if they wish to continue to lead the Utility sector. PG&E is exposed to a few major legal cases which could negatively impact the company. Further, the company must integrate renewable energy resources into the grid while maintaining stability. Analysts are aware of these risks and are divided regarding the future price of PG&E. In conclusion, PG&E the largest utility in the U.S. and is well positioned to take advantage of two major market trends if it can manage the risks. The utility should continue to lead the sector and is a buy if an investor is looking for dividend capture and stable growth in the U.S. utility space. Disclosure: The author has no positions in any stocks mentioned, and no plans to initiate any positions within the next 72 hours. (More…) The author wrote this article themselves, and it expresses their own opinions. The author is not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). The author has no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article. Scalper1 News
Scalper1 News